Carbohydrates often get a bad rap in the world of nutrition, but not all carbs are created equal. Understanding the difference between good carbs and bad carbs is crucial for making informed dietary choices that support your health and wellness goals. This guide will help you navigate the world of carbohydrates and make the best choices for your body.
What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates, or carbs, are one of the three macronutrients essential for human health, alongside proteins and fats. They are the body’s primary source of energy, fueling everything from daily activities to intense workouts1. Carbs are found in a wide variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products.
Good Carbs: The Nutrient Powerhouses
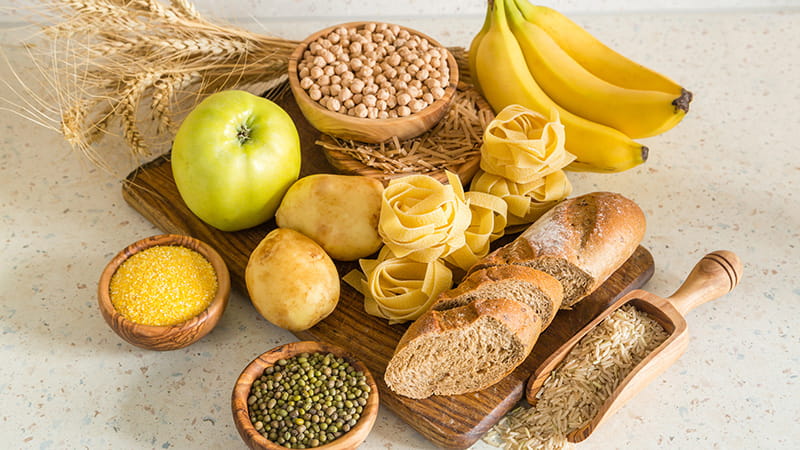
Good carbs, also known as complex carbohydrates, are found in whole, unprocessed foods. These carbs are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients that support overall health2. Here are some key characteristics of good carbs:
1. High Fiber Content
Good carbs are typically high in fiber, which aids in digestion, helps regulate blood sugar levels, and keeps you feeling full longer2. Examples include whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables.
2. Minimal Processing
Whole foods like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat products retain their natural nutrients and fiber because they undergo minimal processing2. This makes them more nutritious compared to their refined counterparts.
3. Low Glycemic Index
Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels3. This helps maintain steady energy levels and reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes. Examples include sweet potatoes, lentils, and most fruits.
4. Rich in Nutrients
Good carbs are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health2. For instance, fruits and vegetables provide vitamins A, C, and K, as well as potassium and magnesium.
Bad Carbs: The Empty Calories
Bad carbs, also known as simple or refined carbohydrates, are often found in processed foods that have been stripped of their natural nutrients4. These carbs can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and provide little to no nutritional value. Here are some characteristics of bad carbs:
1. Low Fiber Content
Refined carbs, such as white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals, have had their fiber removed during processing4. This lack of fiber can lead to digestive issues and rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
2. High Glycemic Index
Foods with a high glycemic index cause quick spikes in blood sugar levels, followed by rapid drops3. This can lead to energy crashes and increased hunger, promoting overeating and weight gain. Examples include white bread, sugary snacks, and soda.
3. Nutrient Deficiency
Bad carbs are often low in essential nutrients and high in empty calories4. Consuming these foods regularly can lead to nutrient deficiencies and contribute to various health issues, including obesity and heart disease.
4. Added Sugars
Many bad carbs contain added sugars, which can contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and increased risk of chronic diseases4. Common sources include candy, baked goods, and sweetened beverages.
How to Choose Good Carbs
Making the right carbohydrate choices can significantly impact your health. Here are some tips to help you choose good carbs:
1. Read Labels
Check food labels for fiber content and added sugars. Aim for foods with high fiber and low added sugars2.
2. Choose Whole Grains
Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat products instead of refined grains2. Whole grains retain their natural nutrients and fiber.
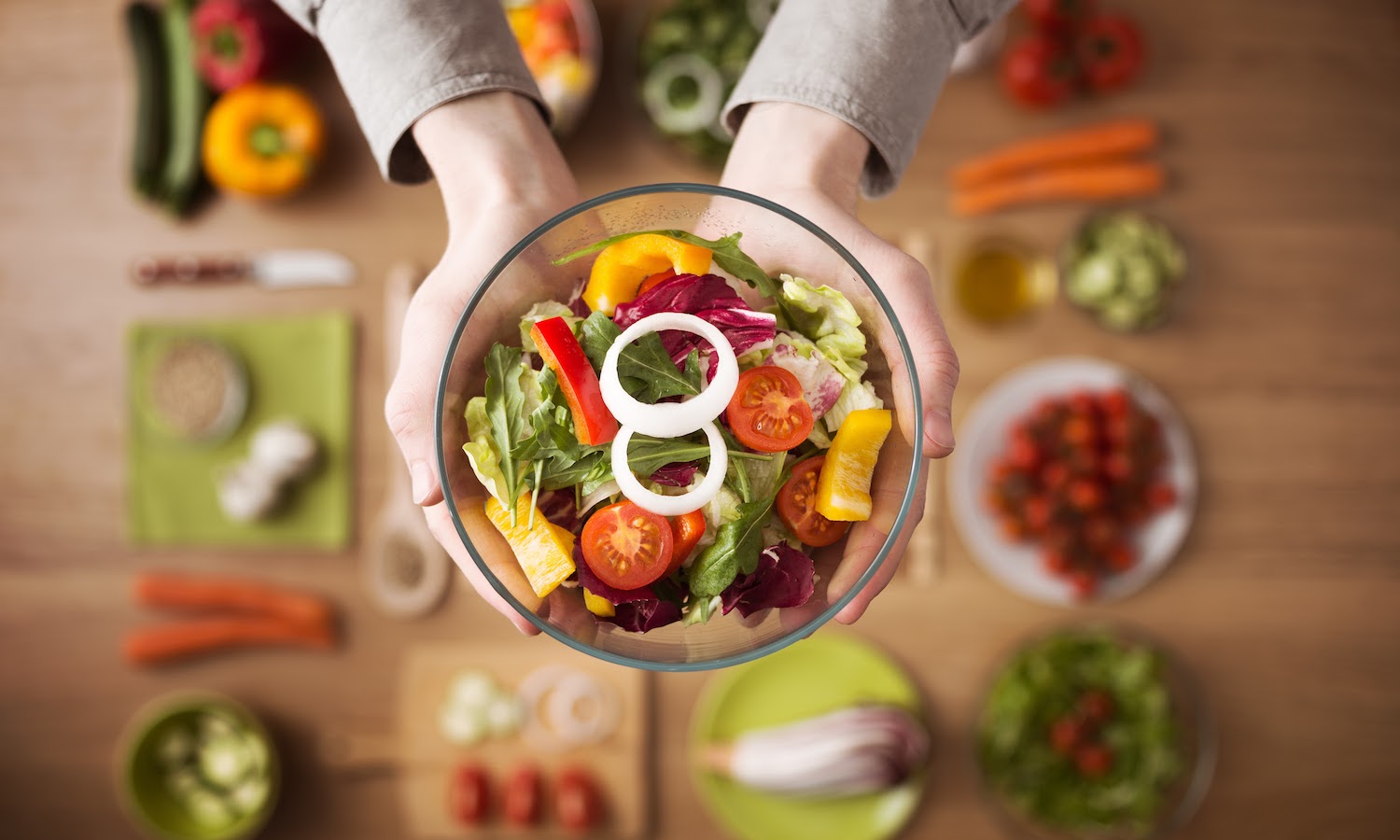
3. Eat a Rainbow
Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet. Each color represents different phytonutrients and antioxidants that benefit your health2.
4. Limit Processed Foods
Reduce your intake of processed foods and sugary snacks. Instead, focus on whole, unprocessed foods that provide essential nutrients2.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between good carbs and bad carbs is essential for making informed dietary choices. Good carbs, found in whole, unprocessed foods, provide essential nutrients, fiber, and sustained energy. In contrast, bad carbs, found in processed foods, can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and offer little nutritional value. By choosing good carbs, you can support your overall health and well-being.